What Is Ice: A Comprehensive Examination Of Its Properties, Formation, And Uses
FAQ
This comprehensive FAQ section provides concise and informative answers to common questions about the nature, formation, and applications of ice.
Question 1: What is the chemical composition of ice?
Answer: Ice is composed of frozen water molecules (H2O). When water freezes, the individual H2O molecules form a crystalline lattice structure through hydrogen bonding.

The Triangle and Its Properties CBSE Class 7 Maths Worksheet - Source www.class1to12.com
Question 2: How does ice form?
Answer: Ice forms when water solidifies, either through a process called freezing or deposition. Freezing occurs when liquid water is cooled to its freezing point and below. Deposition occurs when water vapor directly condenses into ice crystals without passing through the liquid phase.
Question 3: What are the different types of ice?
Answer: There are numerous types of ice, each with distinct properties and crystalline structures. Some common types include hexagonal ice (ordinary ice), cubic ice, and amorphous ice.
Question 4: What are the physical properties of ice?
Answer: Ice has unique physical properties, including a high density, low thermal conductivity, and high latent heat of fusion. These properties contribute to its ability to float on liquid water and its insulating properties.
Question 5: What are the various uses of ice?
Answer: Ice has numerous applications, such as cooling and preservation of food and beverages, ice skating, ice sculptures, and scientific research. Its unique properties make it valuable in various industries and everyday life.
Question 6: How can ice impact the environment?
Answer: Ice plays a crucial role in the Earth's ecosystems. It influences climate regulation, ocean currents, and habitats for various species. Understanding the effects of ice on the environment is essential for addressing climate change and its consequences.
This FAQ section provides a concise introduction to the fascinating world of ice and its multifaceted nature. Further exploration into this topic can reveal even more intriguing insights.
Transition to the next article section: Exploring the Diverse Applications of Ice in Modern Industries →
Tips
To delve deeper into the fascinating subject of ice, What Is Ice: A Comprehensive Examination Of Its Properties, Formation, And Uses provides a wealth of information. This article offers insights into ice's unique characteristics, how it forms, and its diverse applications.
Tip 1: Explore the remarkable properties of ice.
Ice possesses a range of exceptional properties that distinguish it from other substances. Learn about its unique crystalline structure, high thermal conductivity, and low density. These properties contribute to ice's ability to float on water and act as an effective insulator.
Tip 2: Understand the process of ice formation.
The formation of ice is a captivating natural phenomenon. Dive into the science behind freezing, the role of temperature, and the influence of pressure. Discover how these factors affect the size, shape, and appearance of ice crystals.
Tip 3: Discover the practical applications of ice.
Ice finds uses in various domains, including refrigeration, construction, and medicine. Learn how ice is employed in cooling systems, preserving perishable goods, and creating slippery surfaces for sports and recreation. Explore the therapeutic applications of ice in reducing inflammation and alleviating pain.
Tip 4: Investigate the environmental significance of ice.
Ice plays a vital role in shaping the Earth's ecosystems. Delve into the importance of ice caps, glaciers, and sea ice for regulating global temperatures and supporting diverse wildlife. Discover the impact of climate change on ice formations and its far-reaching consequences.
Tip 5: Appreciate the cultural and historical aspects of ice.
Ice has captivated human imagination throughout history. Learn about the cultural significance of ice in art, literature, and mythology. Explore the role of ice in traditional practices, such as ice harvesting and winter sports. Discover how ice has influenced human interactions and shaped cultural landscapes.
These tips provide a starting point for exploring the fascinating world of ice. To gain a comprehensive understanding of this remarkable substance, delve into the article's detailed examination of its properties, formation, and uses.
What Is Ice: A Comprehensive Examination Of Its Properties, Formation, And Uses
Ice is a solid form of water that occurs naturally on Earth and other planets. It is an essential part of the Earth's climate system and plays a crucial role in many natural and human activities. Understanding the properties, formation, and uses of ice is vital for various scientific disciplines and practical applications.
- Structure: Ice forms when water molecules arrange themselves into a crystalline lattice.
- Properties: Ice is generally transparent, hard, and brittle, with a low density and thermal conductivity.
- Formation: Ice forms when water freezes due to a decrease in temperature or an increase in pressure.
- Types: There are various types of ice, including sea ice, glaciers, permafrost, and snow.
- Uses: Ice has numerous applications, such as cooling, refrigeration, transportation, and construction.
- Climate Impact: Ice plays a significant role in regulating Earth's temperature and sea levels.
These key aspects provide a comprehensive understanding of ice, its characteristics, and its significance in various contexts. Ice's unique structure, properties, and formation processes make it an essential component of the Earth's ecosystems and a valuable resource for human activities. Understanding these aspects contributes to scientific advancements in climate science, cryology, and engineering, enabling us to harness the benefits of ice while mitigating its potential risks.

Neurological examination what it is and its importance by Salubritas - Source issuu.com

Cross-examination And Its Legal Provisions Under Indian Law-EvidenceAct - Source www.lawnn.com
What Is Ice: A Comprehensive Examination Of Its Properties, Formation, And Uses
Ice is a naturally occurring solid form of water that forms when water is frozen below its freezing point of 0 degrees Celsius (32 degrees Fahrenheit). It is composed of water molecules that are arranged in a crystalline structure, held together by hydrogen bonds. The physical properties of ice vary depending on its temperature and pressure, but it is generally a hard, brittle, and transparent material. Ice plays a crucial role in the Earth's climate system, influencing weather patterns, ocean currents, and sea levels. It is also used for various practical applications, such as refrigeration, ice skating, and scientific research.
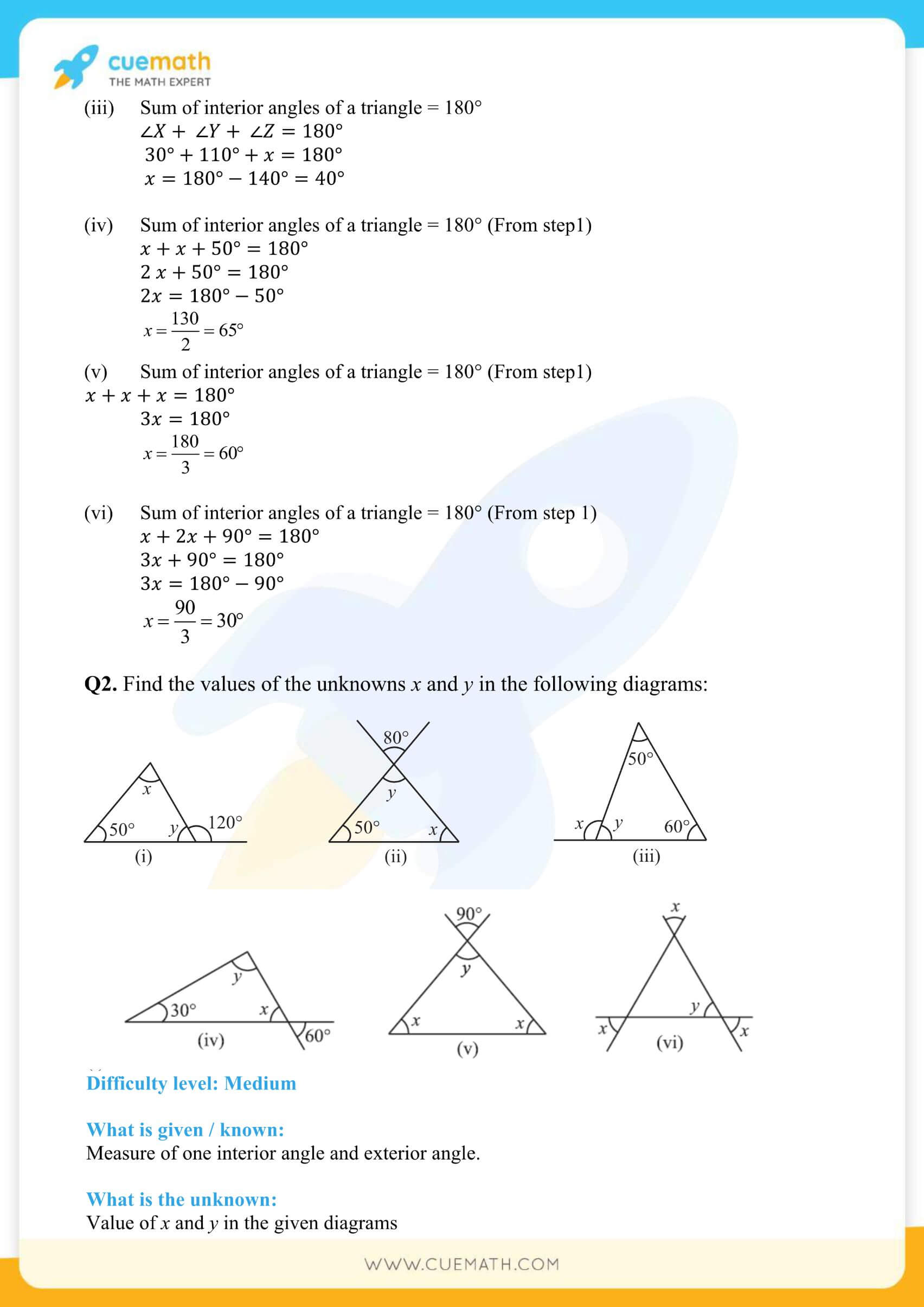
Grade 7 Triangle And Its Properties - Source vivibrodetd3dblearning.z14.web.core.windows.net
Understanding the properties, formation, and uses of ice is essential for comprehending its significance in the Earth's systems and human activities. The study of ice provides insights into the behavior of water under different conditions, contributing to our knowledge of hydrology, climatology, and glaciology. Furthermore, the practical applications of ice have facilitated advancements in refrigeration, transportation, and even medical procedures.
In conclusion, "What Is Ice: A Comprehensive Examination Of Its Properties, Formation, And Uses" serves as a valuable resource for exploring the multifaceted nature of ice, its impact on the environment, and its practical significance in various fields.
Table: Properties, Formation, and Uses of Ice
| Property | Formation | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Crystalline structure | Freezing of water at or below 0°C (32°F) | Refrigeration |
| Hardness | Compression of snow or freezing of water under pressure | Ice skating |
| Brittleness | Rapid cooling or mechanical stress | Scientific research (e.g., cryogenics) |
| Transparency | Alignment of water molecules in crystalline structure | Lenses and optical instruments |
| Density | Varies with temperature and pressure | Insulation and construction |
| Thermal conductivity | Low thermal conductivity | Insulation and cooling |
| Melting point | 0°C (32°F) at atmospheric pressure | Ice cream and beverages |
| Sublimation point | Direct transition from solid to gas at low pressure | Freeze-drying and vacuum packaging |
Zeb Powell: From Space Camp To Space Pioneer, Kick Off Destiny: Unlocking The Power Of Determination And Perseverance, 14th Amendment: Citizenship Rights And Equal Protection Under The Law, Super Bowl Triumphs: Tracing The Legacy Of Patrick Mahomes, Clark Hunt: Owner Of The Kansas City Chiefs, Driving Success And Legacy, Jason Kidd: NBA Legend And Coaching Phenom, Real-Time Apple (AAPL) Stock Price: Analysis And Market Updates, Demarvion Overshown: Versatile Linebacker With NFL Potential, Marketplace Insurance: Find Affordable Health Coverage For Individuals And Families, Iowa Hawkeyes Take On Ohio State Buckeyes In Epic College Football Clash,